What is a bearing?
Bearing Types and Classification

Bearings are used in many machines that work or are operated in circular or axial motion. The main duty of bearings is; The aim is to ensure that the required movement is transmitted with the least possible friction, that is, with the least compromise on power.
bearingIn the picture above, you see a simple bearing formed by interlocking an inner ring and an outer ring. In order for these rings to rotate easily within each other, there is a series of rollers placed in between. It is vital for the quality and life of the bearing that all of these rollers are placed very aligned and smooth, with the same size and smoothness. Naturally, factories with the highest technology can easily produce the highest quality bearings.
To give an example of bearings that everyone can understand, there is a bearing in the center of the wheel of a bicycle, on the shaft to which the rim is attached. These bearings support the wheel shaft and enable the wheel to rotate easily around its axis. At this point, the higher quality and frictionless the bearing, the easier the movement will be transmitted from the pedals to the bike. These bearings used in bicycles are not roller bearings as in the picture above, they are ball bearings.
Classification of Bearings
According to the type of rolling elements:
-Ball Bearings
-Roller Bearings
According to the loads they are exposed to:
-Radial
-Axial
Ball Bearings(Radial)

Ball bearings have the highest speed limit of all bearing types. In this type of bearings, due to the spherical structure of the balls, only the upper point of the balls contacts the ring bearings. Therefore, since they provide less surface contact than roller bearings, higher rpm numbers can be achieved with less friction. Depending on the radial clearance, they can be installed obliquely under angle for 8-16 minutes depending on the axis position under normal operating conditions. In standard mass production programs, there are generally single row ball bearings with non-contact covers, as well as bearings with contact seals. Bearings with covers on both sides do not require maintenance and are suitable for operation in environmental conditions between 20-120 (253K-293K). The radial load carrying capacity of double row Ball bearings is higher than single row ones, but they can carry less load axially. It is not suitable for inclined positions.
Ball Bearings(Axial)
Thrust ball bearings can be disassembled. These bearings are manufactured in types that can work in both single and double directions. One-way thrust bearings consist of shaft ring, ball set and body ring. The parts of double-direction thrust bearings are two body rings, two ball sets and spacer rings. Both types of bearings can carry large axial loads.
Shoulder Ball Bearings
Its structure differs from single row ball bearings in that it has a single shoulder on the outer ring. Axial loads can be carried to a limited extent. The ball cage, inner ring and outer ring are interchangeable and are installed separately. In this way, tight bearing is possible for both rings and provides great benefit in serial assembly.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
They are manufactured as single row and double row angular contact ball bearings.
Single row angular contact ball bearings: They can only carry axial loads from one direction and therefore must be mounted next to a second bearing. Single row angular contact ball bearings are not disassembled. The load angle is 40. The most appropriate load distribution is achieved when the force ratios are 1 (Fa / Fr = 1). It is suitable for operation at high speeds and the distance to the opposing bearings should be chosen short. Because the length changes of the shaft due to heat affect the working gap in the bearing. Single row angular contact ball bearings with two-piece inner rings and load angles of 35 are called four-point contact bearings. It has high carrying capacity and can absorb axial loads in both directions. In addition, four-point contact bearings are suitable for operation at high speeds. The best working condition is where the force ratio is 1.27 (Fa / Fr = 1.27).
Double row angular contact ball bearings: The standard type of double row angular contact ball bearings are not disassembled and the load angle is 32. These bearings are also available in split types with a two-piece inner ring and the force angle is 45. They can carry axial loads in both directions and to the same degree.
Self-aligning Ball Bearings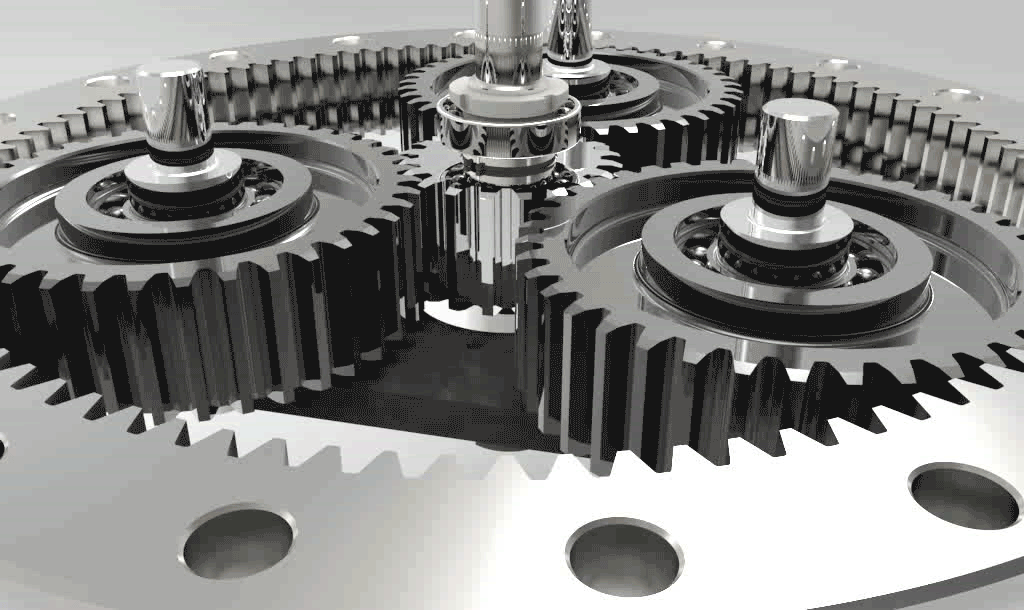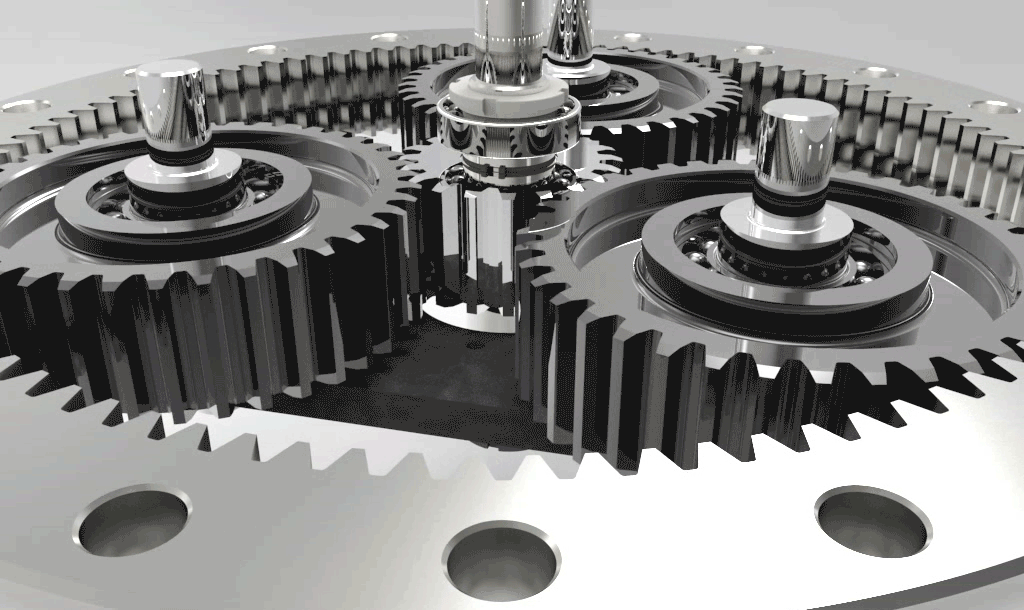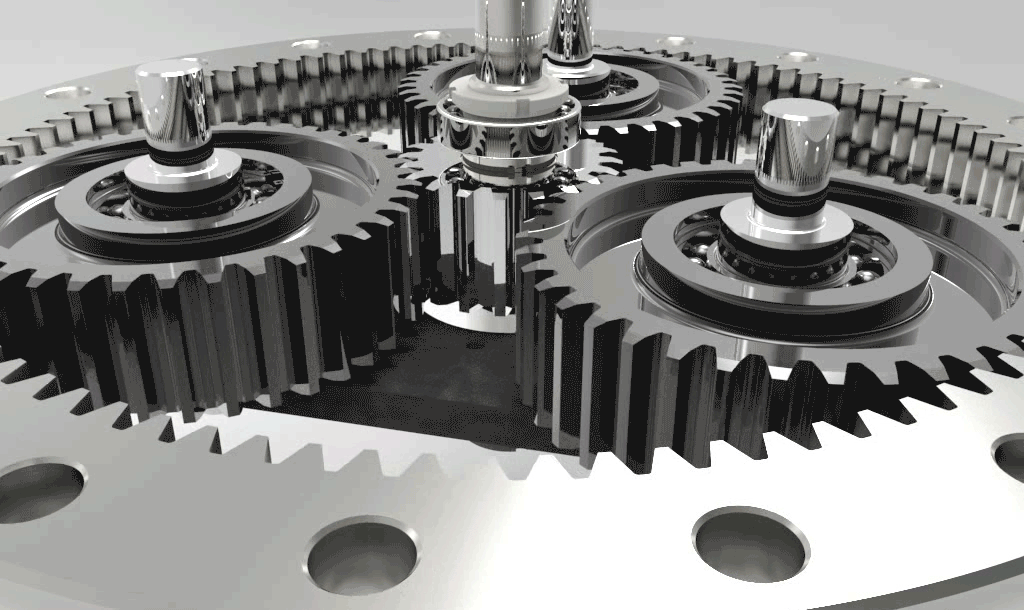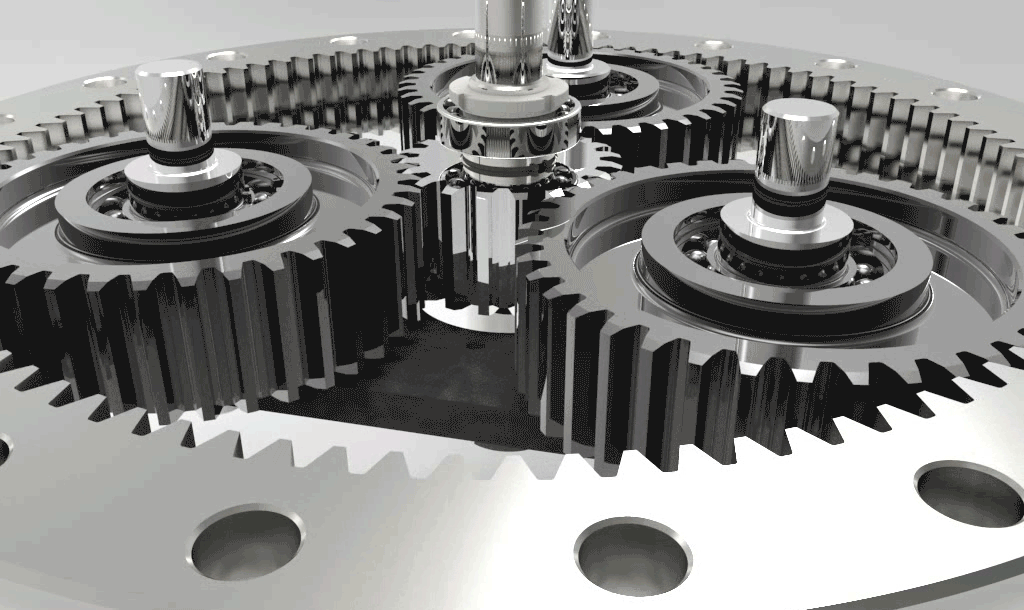
Self-aligning ball bearings are double-row, separable bearings with a concave spherical raceway in the outer ring. Therefore, the angles can be adjusted. Self-aligning ball bearings with wide inner rings are suitable for installation with shafts manufactured in tension form. The inner ring, which is installed in the fixing space on one side of the inner ring, is prevented from rotating on the shaft. If two self-aligning ball bearings with wide inner rings are to be used for a bearing, the retaining pins must be installed either inwards or outwards.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings are radial bearings that can be disassembled. The linear contact between the rollers and the raceways was brought to the appropriate shape and the stresses were eliminated in this way. A curvature of 2-4 minutes is allowed for the radial load carrying capacity. These bearings are much more durable than ball bearings. They are very difficult to disperse.
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings are double-row bearings with a concave spherical raceway in the outer ring and cannot be disassembled. That's why your bearings are adjustable. They are not affected by axis errors in bearings and shaft deflections up to 0.5 relative to the axis. Lubrication problems may occur if large bearings are operated at loads close to their strength limits. Generally, the lubrication channel or lubrication hole located on the outer ring provides a solution to the problem.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings can be disassembled. The linear contact between rollers and raceways is optimized. Edge stresses were eliminated in this way. Tapered roller bearings can carry axial loads in one direction. A second tapered roller bearing can be used as a counter support. Length changes in the shaft due to heat negatively affect the bearing clearance required for the bearing to operate. Therefore, the distance to the opposing bearing must be kept small. The bearing clearance is adjusted according to the opposing bearing during assembly.
 ]
] 


